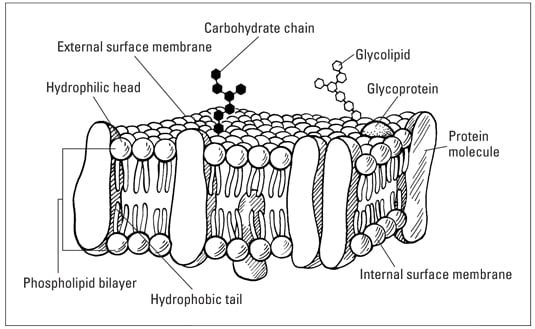
40 label the hydrophobic and hydrophobic portions of the phospholipids
Cell Membrane Function and Structure - ThoughtCo 7.10.2019 · Microscopic view of phospholipids. Stocktrek Images / Getty Images. Phospholipids are a major component of cell membranes.Phospholipids form a lipid bilayer in which their hydrophilic (attracted to water) head areas spontaneously arrange to face the aqueous cytosol and the extracellular fluid, while their hydrophobic (repelled by water) tail areas face … PDF Name Date Per Cell Membrane Structure and Function Label the hydrophobic and hydrophobic portions of the phospholipids. Match the cell membrane structure or its function with the correct letter from the diagram. _____ Attracts water _____ Repels water _____ Helps maintain flexibility of membrane _____ Makes up the bilayer (2 answers) _____ Involved in cell-to-cell recognition
Phospholipids - Types, Functions and their Properties - An Overview - BYJUS Phospholipids are compound lipids, consisting of phosphoric acids, nitrogen base, alcohol and fatty acids. These compound lipids are major components of the cell membrane and also provide a fluid character to the membranes. In cell membranes, these phospholipids have a hydrophilic head and a hydrophobic tail, which forms the inside of the bilayer.

Label the hydrophobic and hydrophobic portions of the phospholipids
Phospholipid Bilayer | Introduction, Structure and Functions Phospholipid Bilayer. The phospholipid bilayer comprised of two end-to-end phospholipids sheets which assemble from tail to tail order. The Hydrophobic tails attached with each other, establishing the interior side of the membrane. The Polar heads commerce the fluid inside and outside environment of the Cell. Answered: Identify the hydrophobic and… | bartleby Solution for Identify the hydrophobic and hydrophilic region(s) of a phospholipid. close. Start your trial now! First week only $4.99! ... draw the structure of phospholipids. ... Label which end is polar and which one is nonpolar. Identify which end is known as being hydrophobic and which end is known as being hydrophilic. arrow_forward. Why are phospholipids hydrophilic? - FindAnyAnswer.com 1: A phospholipid consists of a head and a tail. The "head" of the molecule contains the phosphate group and is hydrophilic, meaning that it will dissolve in water. The "tail" of the molecule is made up of two fatty acids, which are hydrophobic and do not dissolve in water. One may also ask, why are hydrophilic heads important?
Label the hydrophobic and hydrophobic portions of the phospholipids. Solved Match the cell membrane structure or its function | Chegg.com Question: Match the cell membrane structure or its function with the correct letter from the diagram Label the hydrophobic and hydrophobic portions of the phospholipids. 10 draw and label a phospholipid show the hydrophobic Label this diagram of the plasma membrane with the following terms: glycoprotein, cholesterol, hydrophilic region, hydrophobic region. Phospholipid bilayer, protein molecules. a. hydrophobic region b. hydrophilic region c. phospholipid bilayerd. cholesterol e. protein molecules f. protein End of preview. Want to read all 2 pages? (Solved) - Which of the following statements is TRUE of ... - Transtutors Draw a membrane that includes the following components: phospholipids, trans membrane proteins, peripheral membrane proteins. Label the hydrophobic core (hydrophobic interior) of your membrane. 2.Explain the orientation of phospholipids in a membrane. 3.Describe the mobility of phospholipids and membrane proteins in the plasma membrane. Phospholipids - Structure, Types, Properties and Function Let us know some key points on phospholipids here. A glycerol molecule, two fatty acids, and an alcohol-modified phosphate group constitute phospholipids. The phosphate group is a hydrophilic, negatively charged polar head. Hydrophobicity is found in the uncharged, nonpolar tails of fatty acid chains.
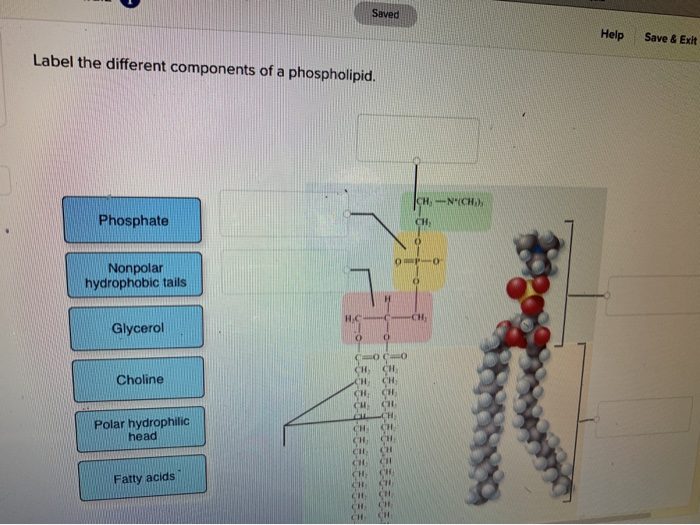
phospholipid | biochemistry | Britannica This amphipathic nature (containing both hydrophobic and hydrophilic groups) makes phospholipids important in membranes; they form a two-layer structure, called the lipid bilayer, with the polar head facing out on each surface to interact with water, and with the neutral "tails" driven inward and pointing toward one another. How Phospholipids Help Hold a Cell Together - ThoughtCo Phospholipids belong to the lipid family of biological polymers. A phospholipid is composed of two fatty acids, a glycerol unit, a phosphate group, and a polar molecule. The polar head region in the phosphate group of the molecule is hydrophillic (attracted to water), while the fatty acid tail is hydrophobic (repelled by water). Solved Phospholipid labeling Label the parts of the | Chegg.com Expert Answer. Who are the experts? Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. 100% (14 ratings) Transcribed image text: Phospholipid labeling Label the parts of the phospholipid. Previous question Next question. Is cholesterol a hydrophobic or a hydrophilic substance? Cholesterol is an amphipathic molecule like phospholipids, it contains a hydrophilic and a hydrophobic portion. Its hydroxyl (OH) group aligns with the phosphate heads of the phospholipids. The remaining portion of it tucks into the fatty acid portion of the membrane. Emily approved September 8, 2017. Write your answer.
Glycerophospholipid - Wikipedia The phosphate ester portion ("head") is hydrophilic, whereas the remainder of the molecule, the fatty acid "tail", is hydrophobic. These are important components for the formation of lipid bilayers. Phosphatidylethanoamines, phosphatidylcholines, and other phospholipids are examples of phosphatidates. Phosphatidylcholines Phospholipid Structure & Function | What is a Phospholipid? Phospholipids have both a hydrophobic tail and a hydrophilic head. Hydrophobic means water fearing, in other words, the fatty acid tail (the hydrophobic portion of the phospholipid) does not mix... The Lipid Bilayer - Molecular Biology of the Cell - NCBI Bookshelf Membrane Lipids Are Amphipathic Molecules, Most of which Spontaneously Form Bilayers. Lipid—that is, fatty—molecules constitute about 50% of the mass of most animal cell membranes, nearly all of the remainder being protein.There are approximately 5 × 10 6 lipid molecules in a 1 μm × 1 μm area of lipid bilayer, or about 10 9 lipid molecules in the plasma membrane of a … Correct Phospholipids have a hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tails The ... Plasma membrane is made up of Phospholipids which have two parts: Hydrophilic (consist of phosphate group known as head part) and hydrophobic ( non polar fatty acids known as tail part). Phospholipids heads face outward as they are attractive towards water in intercellular and extracellular fluid and tail part of Phospholipids face inwards.
(PDF) Biochemistry FOR DUMmIES | Sabrina Marie Jade Academia.edu is a platform for academics to share research papers.
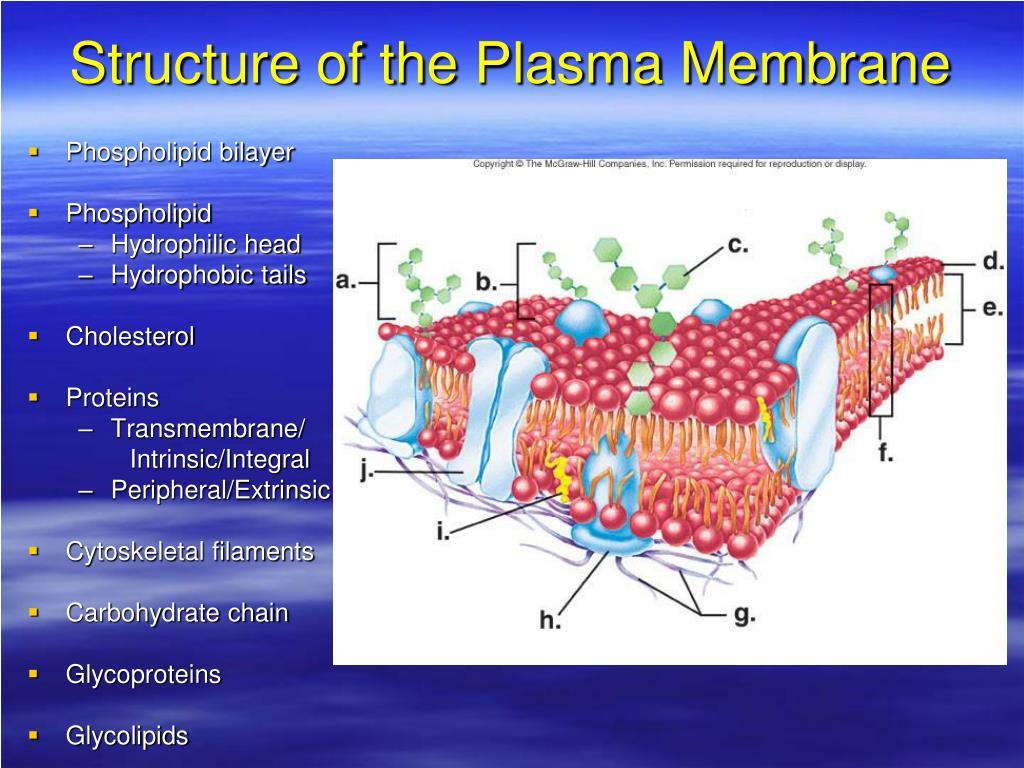
Phospholipid Bilayer | Lipid Bilayer | Structures & Functions The Structure Of The Phospholipid Bilayer Functions Of The Phospholipid Bilayer 1. Maintain The Shape Of The Cell 2. Act As A Semipermeable Membrane 3. Important In Cell Recognition And Communication 4. Maintain Its Internal Environment What else are found in the Plasma Membrane? 1. Cholesterol 2. Glycoproteins 3. Antigens References
Chapter 7 - Lipids - CHE 120 - Introduction to Organic Chemistry ... 18.4.2022 · Often, the ionic part is referred to as hydrophilic, meaning “water loving,” and the nonpolar part as hydrophobic, meaning “water fearing” (repelled by water). When allowed to float freely in water, polar lipids spontaneously cluster together in any one of three arrangements: micelles, monolayers, and bilayers (Figure 7.5 "Spontaneously Formed Polar Lipid Structures …
Phospholipid: Definition, Structure, Function, Examples - Science Terms A phospholipid consists of two basic parts: the head and the tail. The hydrophilic head consists of a glycerol molecule bound to a phosphate group. These groups are polar and are attracted to water. The second group, the hydrophobic tail, consists of two fatty acid chains. Some species use three fatty acid chains, but two is most common.
How a Phospholipid Bilayer Is Both Hydrophobic and Hydrophilic A phospholipid is named for its two main parts, a phosphate group and a lipid. It's usually drawn with the phosphate group as a circle, and this is referred to as the hydrophilic head. Due to its...
The Lipid Bilayer - Molecular Biology of the Cell - NCBI Bookshelf Being cylindrical, phospholipid molecules spontaneously form bilayers in aqueous environments. In this energetically most-favorable arrangement, the hydrophilic heads face the water at each surface of the bilayer, and the hydrophobic tails are shielded from the water in the interior. The same forces that drive phospholipids to form bilayers also provide a self-healing property.
Phospholipid bilayer | Biology Quiz - Quizizz The presence of double bonds in the fatty acyl tail will. answer choices. A. decrease fluidity because of the attraction between the unsaturated tails. B. increase fluidity due to the difficulty of the kinked acyl tail to interact. C. decrease fluidity by increasing the space between the phospholipids.
Phospholipid: Definition, Structure, Function - Biology Dictionary Hydrophobic - a molecule that "hates water"; it is not attracted to water, but will usually dissolve in oils or fats. Lipid bilayer - a double layer of phospholipids that makes up the cell membrane and other membranes, like the nuclear envelope and the outside of mitochondria. Quiz 1. Which is NOT a component of a phospholipid? A. Glycerol


Post a Comment for "40 label the hydrophobic and hydrophobic portions of the phospholipids"