39 internal structure of a clam labeled
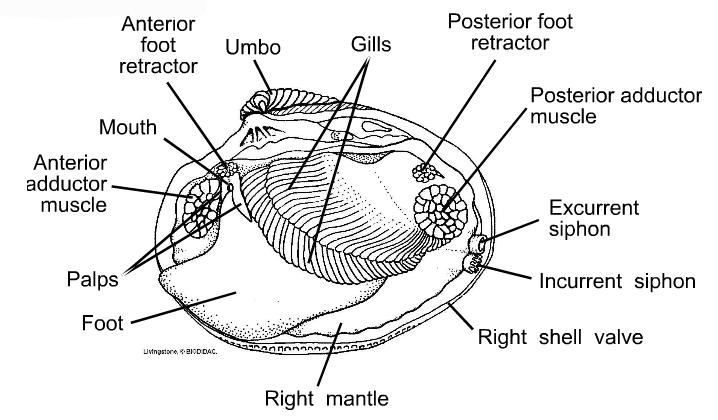
PDF Taxonomy, Anatomy, and Biology of the Hard Clam Internal Clam 1 Mantle Shell Anatomy • Covers visceral or body mass • Holds in fluid • Secrets new shell 2. Ant. adductor muscle 3. Post adductor musclePost. adductor muscle • Hold valves shut 4. Pericardium cavity • Region covered with thin Region covered with thin, dark membrane • Contains 2-chambered heart and kidney in a fluid-filled sac 5. label the internal structures of the clam label the internal structures of the clamshop architects curbed. label the internal structures of the clam
Internal Structure of the Clam 09 3 - YouTube Here is the internal structure of the Clam part 3 for Tim Revell's Bio 2 class Spring 2009.

Internal structure of a clam labeled
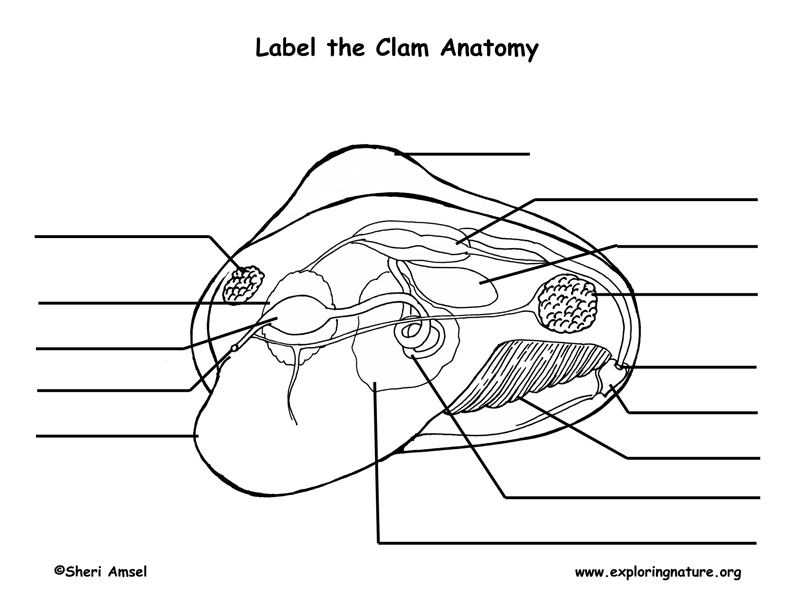
Clam Diagram & Parts | What Is a Clam? | Study.com Belonging to a diverse group of animals known as bivalves, clams can be identified by the presence of two valves, or shells, joined by a hinge that allows the two shells to open or close. A... › books › NBK26869An Overview of the Cell Cycle - Molecular Biology of the Cell ... The two gap phases serve as more than simple time delays to allow cell growth. They also provide time for the cell to monitor the internal and external environment to ensure that conditions are suitable and preparations are complete before the cell commits itself to the major upheavals of S phase and mitosis. PDF Label the Clam Anatomy @Sheri Amsel Label the Clam Anatomy @Sheri Amsel . Created Date: 6/8/2018 3:46:07 PM
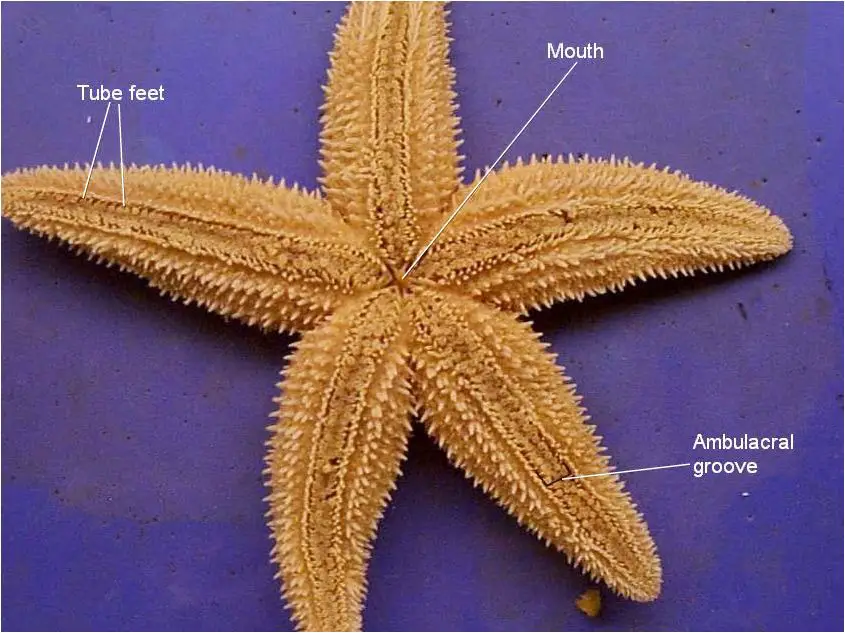
Internal structure of a clam labeled. Clam Dissection: A first introduction to anatomy - Rosie Research This is a long thin strand of muscle that is often wavy and the part of the clam that you can see when the shell is slightly open. This is known as the dorsal body, and it is like a robe that covers the internal organs of the clam. Over time, the mantle secretes what will become the shell, allowing the animal to grow a larger home. Foot Clam Dissection - BIOLOGY JUNCTION Clams are marine mollusks with two valves or shells. Like all mollusks, a clam has a mantle which surrounds its soft body. It also has a muscular foot which enables the clam to burrow itself in mud or sand. The soft tissue above the foot is called the visceral massand contains the clam's body organs. Taxonomy Kingdom -Animalia Phylum - Mollusca successessays.comSuccess Essays - Assisting students with assignments online Get 24⁄7 customer support help when you place a homework help service order with us. We will guide you on how to place your essay help, proofreading and editing your draft – fixing the grammar, spelling, or formatting of your paper easily and cheaply. PDF Biology 11 Name: Clam Dissection 1 anterior posterior 2. Diagram 2: Clam Internal Anatomy 6. With scissors, cut off the ventral portion of the foot. Use the scalpel to carefully cut the muscle at the top of the foot into right and left halves. 7. Carefully peel away the muscle layer to view the internal organs. 8. Locate the spongy, yellowish reproductive organs. 9.
Mollusk Anatomy | Carlson Stock Art Illustration of the internal structure of a clam. Browse images in the Categories, or enter a search term here to search the image archives. Narrow your search results by separating multiple keywords with a comma. Anatomy of the Geoduck Clam - Fisheries and Oceans Canada Internal Anatomy The inner surface of the valves (shell) is usually rough with a deeply impressed, continuous pallial line (where the mantle was sealed to the shell) and triangular pallial sinus (Fig. 3). At the dorsal surface, the hinge ligament joins the two valves and each valve has a cardinal tooth at the hinge. Clam anatomy and what their organs do by Ethan Enfinger - Prezi The vital Organs. The most important out of all the organs in the clam is the heart which pumps blood to all the other organs allowing them to live. Their is also the nervous system which tell parts of the clam to do certain things. And lastly is the urogenital system which depending on what species of clam can have clear differences between ... en.wikipedia.org › wiki › CatfishCatfish - Wikipedia Catfish (or catfishes; order Siluriformes / s ɪ ˈ lj ʊər ɪ f ɔːr m iː z / or Nematognathi) are a diverse group of ray-finned fish.Named for their prominent barbels, which resemble a cat's whiskers, catfish range in size and behavior from the three largest species alive, the Mekong giant catfish from Southeast Asia, the wels catfish of Eurasia, and the piraíba of South America, to ...
clam internal anatomy clam anatomy clams external diagram flickr foot body fresh water. Strongylocentrotus Spp., Sea Urchin: Model Echinoderm, Facts, Life . urchin sea anatomy internal system geochembio echinoderm morphology strongylocentrotus vascular water body oral facts pole cycle taxonomy game. Clam Dissection - YouTube . clam ... Clam Diagram Labeled - schematron.org on Clam Diagram Labeled. BACKGROUND: Clams are bivalves, meaning that they have shells consisting of two halves, or valves. The valves Draw a picture of what you see and label the following structures: Umbo IV. Data. A. Diagram - See attached diagram. Label the Parts of the Clam Marine Biology, Clams, Science Activities, Juices,. Clam and Squid Anatomy Flashcards | Quizlet internal structure skeleton (squid) Symmetrical heart (squid) pumps blood to the heart (squid) Branchial heart (squid) pumps blood through gills (squid) Ink sac (squid) produces ink (squid) Afferent branchial arteries (squid) pumps blood to gills (squid) Lateral mantle arteries (squid) carries blood to the mantle (squid) Palial cartilage(s) (squid) Clam Dissection.docx - Google Docs Continue following the intestine toward the posterior end of the clam. Find the anus just behind the posterior adductor muscle. Use your probe to trace the path of food & wastes from the incurrent siphon through the clam to the excurrent siphon. Answer the questions on your lab report & label the diagrams of the internal structures of the clam.
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Riftia_pachyptilaRiftia pachyptila - Wikipedia Riftia pachyptila, commonly known as the giant tube worm, is a marine invertebrate in the phylum Annelida (formerly grouped in phylum Pogonophora and Vestimentifera) related to tube worms commonly found in the intertidal and pelagic zones.
Internal Structure of Leaf: Parts, Function, Diagram - Embibe The upper epidermis is made up of a single layer of parenchymatous cells. 2. The cells in the outer wall are thick and are covered with a thick cuticle (a waxy coating). 3. Stomata are usually absent, but in some aquatic plants, stomata can be observed in the upper epidermis. 4. The upper epidermis is devoid of the chloroplast. 5.
How can you label the internal structure of a clam? - Answers A case structure is a control mechanism that allows different executions depending on value of a label. A variation of a case structure is when the execution is presented different and may not ...
PDF Lab 5: Phylum Mollusca - Amherst College 2. Study the figures of the internal structure of the clam. Locate the adductor and retractor muscles. The adductor muscles (which were cut in two to open the shell) close the valves, whereas the retractor muscles pull in the foot. Notice the large mass of the two adductor muscles, which allow for the prolonged closure of the valves.
Clam study: the shell, the internal anatomy and how they feed Clam study: the shell, the internal anatomy and how they feed Summary Compare different sizes of shells and learn about how shells grow. Dissect a clam and discover that inside a familiar clam shell, often seen on the beach, there is a living animal. Identify the major body parts of a clam, and compare their function to equivalent organs in people.
PDF Investigation #5 - Clam Anatomy - COSEE The smallest clam is _____ cm wide and _____ cm long. The average length of all clams measured by the class is _____ cm Inside of the clam: 1). The thin, whitish flesh lining is called the _____. The mantle encloses all the internal organs of the clam. It is also where new shell is made as the clam grows.
PDF Clam Dissection Information Sheet - Internal Anatomy Clam Dissection Information Sheet -Internal Anatomy A. Feeding Mechanism of clam. Food in mucous string Water enters the mantle cavity from the rear and is pulled forward by the beating of cilia to the gills and mouth.
Internal Structure of the Clam 09 2 - YouTube Here is the second part to the Clam dissection for Tim Revell's Bio 2 class Spring 2009.
PDF Anatomy of a Clam - University of Florida Obtain clam specimens (fresh or preserved). 2. Divide the class into small groups (2-4 per group when possible). 3. Prepare one dissection kit, pan, and clean-up materials per group. 4. Copy the dissection guide for each student. 5. Copy the Externaland Internal Clam Anatomyhandouts for each student. 6.

Post a Comment for "39 internal structure of a clam labeled"